Table of Contents
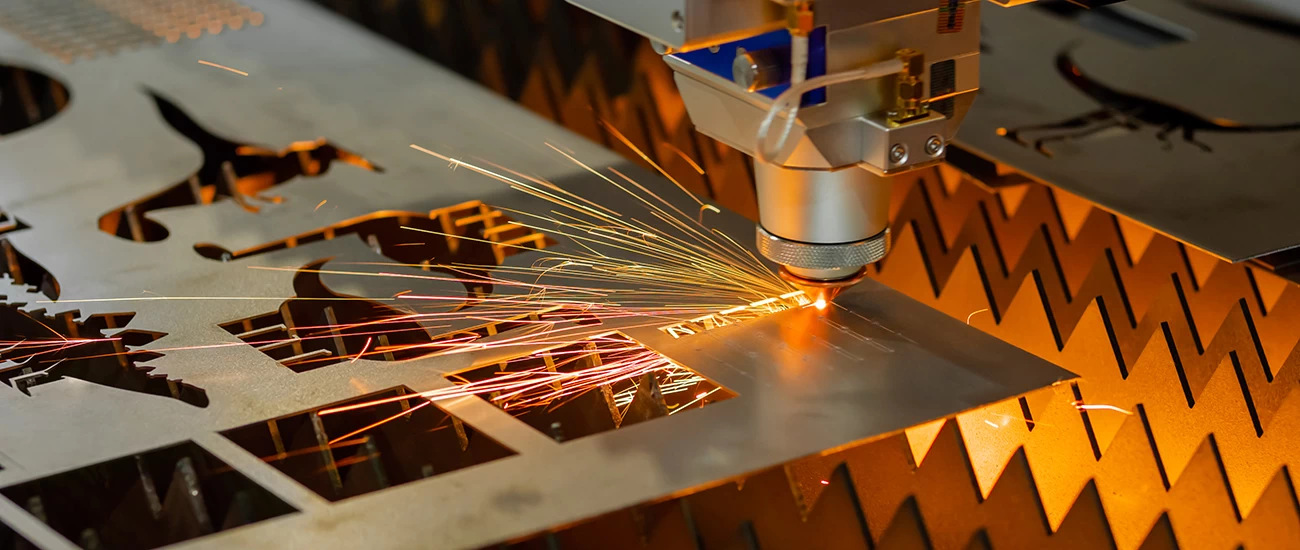
Metal, with its lustrous appearance and ductile properties, holds an irreplaceable position in the realms of craftsmanship and jewelry making. Fueled by modern technology, metal materials are gradually becoming the focus of research and application in laser cutting technology. Laser cutting machines enable unprecedented precision and efficiency in processing various metals, unlocking new possibilities. This article delves into the effects of laser cutting technology on common metals and emphasizes safety considerations during usage.
Principles of Laser Cutting for Metal Materials
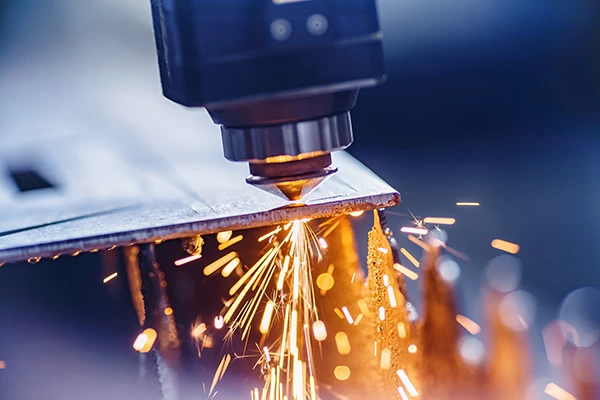

The principles behind laser cutting metal materials involve intricate interactions between metal and light. When a 1064nm laser beam irradiates the metal surface, it exhibits a series of remarkable characteristics in response to the interaction with light waves.
Initially, metals have a low absorption rate of 0.5% to 10% for this wavelength, allowing the laser to penetrate the material without causing surface damage. However, as the laser beam focuses on the metal surface, forming a spot with high power density, the surface rapidly generates thermal energy. This process occurs within microseconds, triggering an instantaneous reaction from the metal.
Metals in a molten state during this process show a significant increase in absorption rate, up to 60% to 80%. This abrupt change leads to the melting of the metal surface, forming a liquid state. In laser cutting, the high-density laser beam scans the metal surface, rapidly heating the material to temperatures ranging from several thousand to over ten thousand degrees Celsius. The intense heat causes the metal material to melt or vaporize, creating a molten or vaporized zone.
To achieve precise cutting, high-pressure gas is introduced into the laser-affected area. The role of these gases is to expel molten or vaporized metal substances from the cutting gap. The flowing force of these high-pressure gases aids in removing melted metal residues and quickly blowing away vaporized substances, achieving a clean and precise cut. Laser cutting technology, with its high control capability and rapid heating characteristics, finds extensive applications in the field of metal processing, opening up new possibilities for the manufacturing industry.
7 Common Metals that Laser Cutting Machines Can Process
Laser cutting technology is widely applied to process both metal and non-metal materials, reducing processing time, lowering costs, and improving workpiece quality. The following section analyzes the processing effects of laser cutting machines on several common metals.
Carbon Steel

Modern laser cutting systems can cut carbon steel plates with a thickness of up to 20mm or even thicker. Oxygen-assisted laser cutting machines can control the cut seams to a satisfactory width, achieving seams as narrow as around 0.01mm for thin plates.
Stainless Steel
Fiber laser cutting machines serve as effective tools for the manufacturing industry. By strictly controlling the heat input during the laser cutting process, the heat-affected zone can be minimized, preserving the excellent corrosion resistance of stainless steel.
Titanium and Titanium Alloys

Pure titanium efficiently couples with focused laser beams, assisting in rapid cutting when using oxygen as the auxiliary gas. However, using air as the auxiliary gas is safer for preventing oxidation on the cut edges.
Aluminum and Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum cutting involves a melting process, with the auxiliary gas mainly used to blow away molten products from the cutting area. Generally, good cutting surface quality can be achieved. For some aluminum alloys, precautions are necessary to prevent the formation of intergranular microcracks on the cut surface.
Copper and Copper Alloys
Pure copper (red copper) cannot be cut with a CO2 laser beam due to its high reflectivity. Fiber laser cutting machines with specific anti-reflection capabilities are required. Brass (copper alloy) can be cut with high-power laser cutting machines, using air or oxygen as the auxiliary gas for cutting thin sheets.
Nickel Alloys
Most nickel alloys can undergo oxidation-melting cutting. They exhibit excellent mechanical, physical, and chemical properties, finding widespread applications in energy development, chemical industry, electronics, navigation, aviation, and aerospace.
Alloy Steel

Most alloy structural steels and alloy tool steels can achieve good cut edge quality with laser cutting. Even high-strength materials can yield straight, slag-free cut edges if process parameters are well-controlled. However, tungsten-containing high-speed tool steels and hot-work steels may experience melting and slagging during laser cutting.
With the rapid development of the laser industry, related technologies and products are becoming increasingly mature. In the field of laser cutting machines, fiber laser cutting machines, with their low maintenance costs and high cutting quality, offer higher cost-effectiveness compared to YAG and CO2 laser cutting machines. They are gaining more market share.
Evaluating the Quality of Metal Laser Cutting Machines
When using a metal laser cutting machine, assessing the quality of the machining involves several key points:

Smooth Cutting Surface, Fewer Patterns, and No Brittle Fracture
When laser cutting a sheet at high temperatures, traces of melted material should not appear below the vertical laser beam, but rather be expelled from the back of the laser beam. To correct this, reduce the feed rate at the end of the cutting process to eliminate the formation of patterns.
Narrow Cut Seam Width
Generally, cut width does not affect cutting quality, except when creating especially precise contours within components. Cut width determines the minimum inner diameter of contours, and as the sheet thickness increases, the cut width also increases. Therefore, to ensure consistent high precision, the working area of the laser cutting machine should remain constant, regardless of the cut width.
Good Verticality of the Cut Seam, Small Heat-Affected Zone
Verticality of the cut edge becomes crucial when processing materials thicker than 18mm. As the laser beam moves away from the focus, it diverges, causing the cut to widen towards the top or bottom, depending on the focus position. Deviation of the cut edge from the vertical line by a few millimeters results in less verticality, affecting cutting quality.
Thermal Effects on Cut Materials
As a thermal cutting processing tool, the metal laser cutting machine inevitably causes thermal effects on materials, reflected in three aspects:
– Thermal affected zone: The area near the cut that is heated during laser cutting.
– Concavities and corrosion: Adversely affect the surface of the cut edge, impacting the appearance of the laser cutting machine.
– Material deformation: If cutting causes a rapid increase in temperature, it may lead to deformation. In fine processing, this is crucial, as contours and connecting pieces are usually only a few millimeters wide. Controlling laser power and using short laser pulses can reduce component heating and prevent deformation.
Safety Considerations When Using Metal Laser Cutting Machines
In the contemporary world of industrial manufacturing, metal laser cutting machines are gradually becoming commonplace. With their advantages of high efficiency, flexibility, and low pollution, they find extensive applications across various industries, especially in the processing of metal materials, bringing higher benefits to numerous metal processing manufacturers. However, users may encounter safety issues during the operation of metal laser cutting machines, some due to improper operation and others resulting from insufficient machine understanding. These issues pose significant risks, emphasizing the importance of early prevention. Let’s explore how users can protect their safety when using metal laser cutting machines.
Top Ten Safety Points for Operating Metal Laser Cutting Machines:

Operator Training
Operators must undergo training to familiarize themselves with the equipment’s structure and performance while acquiring knowledge of the operating system.
Material Handling
Avoid processing materials that can potentially produce smoke and vapor before explicit laser irradiation or heating to prevent potential hazards.
Constant Supervision
Operators must not leave the machine unattended during startup. If necessary to leave, stop the machine or turn off the power switch.
Safety Standards Compliance
Adhere to universal cutting machine safety performance standards. Start the laser according to the specified laser startup procedure.
Fire Prevention
Place fire extinguishers in easily accessible locations. When not in operation, close the laser or shutter. Avoid placing combustible materials such as paper, cloth, or other flammable materials near the unprotected laser beam.
Material Processing Precautions
Avoid processing materials that can potentially produce smoke and vapor before explicit laser irradiation or heating to prevent potential hazards.
Immediate Response to Anomalies
If abnormalities are detected during the processing, immediately shut down the machine and rectify the fault or promptly report to the supervisor.
Personal Protective Equipment
Wear occupational protective equipment as needed and wear compatible laser safety goggles near the laser beam.
Cylinder Handling Precautions
When using gas cylinders, avoid damaging the welding wire to prevent leakage accidents. Cylinder use and transportation must comply with cylinder regulations. Prohibit explosive gas cylinders from exposure to sunlight or heat sources. When opening the bottle valve, the operator should stand beside the bottle mouth.
Maintenance Safety
Adhere to high-pressure safety regulations during maintenance. According to standards and procedures, metal laser cutting machines should undergo maintenance every 40 hours of operation or weekly and major maintenance every 1000 hours of operation or every six months. After turning on the machine power, manually open it at low speed in the X and Y directions and check for abnormalities.
Conclusion
In the current wave of industrial manufacturing, metal laser cutting machines, as a forward-looking technology, provide convenience and efficiency in production across different sectors. However, technological progress must go hand in hand with safe usage. By enhancing understanding of metal laser cutting machines, operating them rationally, and keeping safety points in mind, we can better explore the potential of this technology and drive progress in the manufacturing industry. In the future, with the continuous development of laser technology, metal laser cutting machines will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in innovation and production, injecting new momentum into various industries’ development.











