Table of Contents
Nowadays, plastics have been widely applied in various fields, ranging from daily necessities to scientific domains. Plastics, to realize their utility, are manufactured into various products, and plastic welding stands out as an effective method for the permanent connection of plastic components.
Plastic welding is a plastic joining process based on the self-adhesive principle, where the welding principle involves a phase transition from solid to liquid (melting or dissolving), followed by solidification at the joint interface. The welding of thermoplastic parts relies on the diffusion of polymer chains. It requires high temperature, pressure, and time to achieve a strong mechanical connection. The polymer molecules in thermoplastics have linear or branched structures, and as these molecules are not cross-linked, they are prone to relative sliding. Therefore, the use of thermal energy and continuous stress can induce relative sliding or flow of polymer molecules, thus realizing the welding process.
Several commonly used plastic welding methods in the market include ultrasonic welding, laser welding, hot plate welding, friction welding, vibration welding, and high-frequency welding. This article introduces these commonly used thermoplastic plastic welding processing methods, hoping to provide assistance.
1. Ultrasonic Welding

Principle
Ultrasonic plastic welding is based on the generation of high-frequency sine wave signals by a signal generator. These signals are then converted into high-frequency mechanical vibration energy by a transducer. The amplified vibration is coupled to the plastic part under high pressure through an amplitude rod and welding head. This high-frequency friction causes the plastic contact surface to momentarily generate high-temperature melting. After the ultrasonic stops, the two plastic parts, briefly pressure-sealed and cooled, are welded into one body. The welding process generally does not exceed one second, and the welding strength is comparable to the body.
Advantages
Fast, flexible, stable welding with a short duration; does not require flux or protective gas, and does not produce harmful gases or slag; guarantees product welding quality.
Disadvantages
Requires close contact between welding materials, with specific requirements for material composition, hardness, and size.
Applicable Range
Nylon, polyester, polypropylene, certain polyethylenes, modified acrylic resins, some ethylene-based compounds, amino-formate compounds, etc. Widely used in various industries such as electronics, automotive parts, plastic toys, cultural products, handicrafts, cosmetics, etc.
2. Laser Welding
Principle
The laser-generated beam is focused on the area to be welded through a system of mirrors, lenses, or fiber optics. In the thermal zone formed, the plastic is softened and melted. In the subsequent solidification process, the melted material forms a joint, connecting the components to be welded.
Advantages
Laser welding machine does not need to come into contact with the adhered plastic parts; fast speed, high level of automation, convenient for processing complex plastic components; no burrs; strong and firm welding; high-precision welded parts can be obtained; no vibration technology; can produce airtight or vacuum-sealed structures; minimizes heat damage and deformation; can bond resins with different compositions or colors.
Disadvantages
High initial equipment investment cost; requires special properties of the base material.
Applicable Range
Plastic laser welding technology is widely used in areas such as automotive, medical devices, and packaging.
3. Hot Plate Welding
Principle
Hot plate welding, also known as heat sealing welding, is the simplest plastic welding technology. In the welding process, two plastic parts are required to be sealed into one whole. Generally, a hot-sealing machine is used for operation. The hot-sealing machine uses various external conditions (such as heating methods) to heat the connecting surfaces of the two plastic parts separately. The heated sealing area becomes a viscous flow state, forming a molten layer on the connecting surface. Pressure is applied to make it adhere, and with a certain pressure and time, the two plastic materials are fused into one body. After cooling, it has a certain strength and sealing performance, ensuring that it can withstand external forces during use without cracking or leaking, achieving the purpose of heat sealing.
Advantages
High welding strength, good aesthetics; few defects, can be automated.
Disadvantages
Limited application range, and the workpiece requires a certain flatness.
Applicable Range
This welding method is suitable for materials with low melting points and good plasticity, such as PVC, PE, PP, etc.
4. Friction Welding
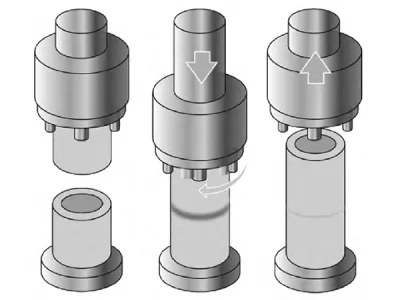
Principle
Friction welding is a method where the frictional heat generated between thermoplastic plastics causes them to melt on the friction surface. Under pressure, they cool and combine. This joining method is called friction welding and is most suitable for cylindrical workpieces.
Advantages
High productivity, convenient for automation and mechanization, good joint performance, simple equipment, easy operation.
Disadvantages
Relies on the rotation of the workpiece, making welding non-circular cross-sections difficult.
Applicable Range
Friction welding technology has a wide range of applications and can weld automotive half shafts, valves, airbags, turbochargers, integral gears, universal joints, front suspensions, etc.
5. Vibration Welding
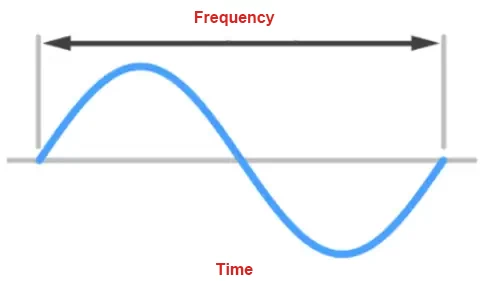
Principle
Vibration welding is also based on the heat generated by the mutual friction of connecting surfaces. Unlike rotational friction welding, friction occurs in a linear direction along the surface. Unlike ultrasonic welding, the vibration frequency is lower, ranging from 120-240Hz. Vibration is generated by the linear relative motion between two plastic parts. Linear friction welding is very flexible and can weld complex-shaped, large-sized parts, which other plastic welding methods cannot achieve.
Advantages
Applicable to almost all thermoplastic plastics; can weld irregular, complex-shaped parts; can weld large parts; easy to achieve automated production.
Disadvantages
Can only accept a welding surface within 10 degrees; plastic parts themselves need to be strong, able to withstand the energy generated by vibration friction, and relatively thin walls are prone to breakage.
Applicable Range
Batteries, automotive radiators, oil pots, other pipeline products and containers, gasoline filters, various types of car lights, automotive motor parts, sensors, curved pipes, nylon products, and nylon weaving products.
6. High-Frequency Welding
Principle
Utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction and high-frequency induction heating technology, it penetrates plastic products to induce bodies or magnetic plastics buried inside the plastic parts to undergo induction heating. The welded plastic can generate heat in a rapidly alternating electric field, causing the welded area to quickly soften and melt. It then fills the gap at the interface and, with the assistance of a sophisticated mechanical device, achieves perfect welding.
Advantages
Accurate positioning, good flexibility, suitable for processing smaller products, high production efficiency, easy to operate.
Disadvantages
Requires specific workpiece sizes; larger workpieces may need multiple welding processes.
Applicable Range
High-frequency plastic welding is used for most plastics, such as ABS, PVC, PP, and PET.
7. Hot Air Welding

Principle
Hot air welding, sometimes called hot gun welding, is similar to oxyacetylene flame welding for metals. It uses a stream of hot air to raise the temperature of the surfaces to be welded and the welding rod, melting the welding rod and fusing it with the base material to achieve welding. During operation, the welding surface is cleaned first, and then hot air is used to simultaneously heat the welding surface and the welding rod. This welding method requires the welding rod and the base material to be the same. If welding different materials, the welding rod should be made of two materials or a blend of the two.
Advantages
Simple equipment, low cost; non-contact welding, does not damage the components; heating and temperature is easy to control.
Disadvantages
Long operation cycle, not suitable for batch processing, welding quality depends on the operator's skills.
Applicable Range
This method can be used for most polymer plastics, including polycarbonate (PC), polystyrene (PS), polyamide (PA), nylon, derivatives, PVC, ABS, etc.
Conclusion
Choosing the right plastic welding method requires considering multiple factors such as material type, component shape, and production requirements. In practical applications, the most suitable welding method can be chosen based on specific conditions to ensure the robustness and quality of the connection. Through continuous technological innovation and research and development, plastic welding technology will demonstrate its application potential in a wider range of fields, bringing more convenience and benefits to modern industry.