Table of Contents
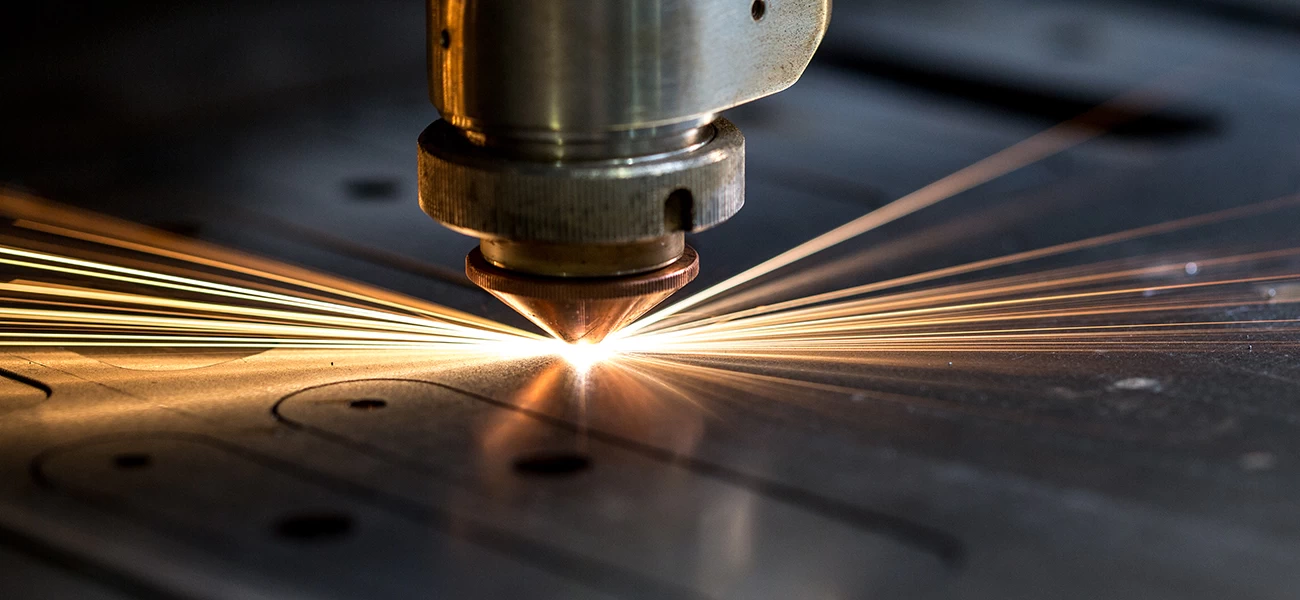
As a significant cutting tool in sheet metal processing, laser cutting machine equipment has brought better cutting results to many customers. With prolonged usage, it’s inevitable for metal laser cutting machines to experience various issues. To reduce the occurrence of faults, users need to perform regular maintenance and upkeep on their equipment.
Any mechanical product requires appropriate maintenance and care, and the same holds true for laser cutting machines. However, users often overlook this aspect, which can lead to a decrease in cutting efficiency and a shortened equipment lifespan. So, how should one go about maintaining and caring for a laser cutting machine?

The primary components of a laser cutting machine include the electrical circuit system, drive system, cooling system, light source system, and dust removal system. The key parts that need regular maintenance are the cooling system (ensuring temperature stability), dust removal system (ensuring effective dust removal), optical system (preserving beam quality), and the drive system (maintaining normal operation). Now, let’s delve into some specific maintenance tips for laser cutting machines.
Maintenance of the Cooling System

The water inside the chiller needs to be regularly replaced. The typical replacement frequency is every two months. The quality and temperature of the circulating water directly impact the lifespan of the laser tube. It is recommended to use pure or distilled water, with the water temperature controlled below 38°C. Prolonged use without water replacement can lead to scale buildup, which can block the waterways, so regular water replacement is essential.
Ensure that water circulation remains unobstructed at all times. The cooling water is responsible for dissipating the heat generated by the laser tube. Higher water temperatures result in lower optical output power (the optimal water temperature range is 18-22°C, with slight variations for different laser systems). If the water supply is interrupted, the accumulated heat inside the laser cavity can cause tube-end rupture and even damage the laser power supply. Therefore, it is necessary to check the cooling water’s flow regularly. In case of kinks or disconnections in the water pipes, leading to pump failure, timely repairs are essential to prevent a decrease in power or potential equipment damage.
Furthermore, during seasons with significant temperature fluctuations or in areas with varying temperatures, although optical fiber laser transmission lines can withstand harsh environments, lasers have specific environmental requirements. Frequent rainfall and high humidity can lead to condensation inside the laser, potentially damaging its electrical and optical components, resulting in reduced laser performance or even laser damage. Therefore, when seasons change or local temperatures fluctuate, temperature adjustments are necessary:
- During summer, the water temperature should be maintained within the range of 27-28°C, and it should not fall below the dew point temperature in the laser environment.
- In winter, the water temperature should be maintained within the range of 20-21°C, and it should not fall below the dew point temperature in the working environment of the processing head.
Maintenance of the Dust Removal System
Over time, dust accumulates in the fan, affecting exhaust and odor removal, as well as generating noise. When you notice reduced suction power or poor exhaust, power off the equipment, disassemble the fan’s intake and exhaust pipes, clean the accumulated dust, invert the fan to clean the blades, and then reassemble. The maintenance interval for the fan is approximately every three months.
Maintenance of the Optical System

After a period of machine operation, dust accumulates on the lens surface due to the working environment. This accumulation reduces the reflectivity of the focusing mirror and the lens’s transmittance, ultimately affecting the laser’s working power. In this case, clean the lens carefully using lint-free cotton dipped in ethanol or acetone. Handle the lens gently to avoid surface damage, take care during cleaning to prevent drops, and ensure the concave side of the focusing lens faces downward. Additionally, try to minimize high-speed piercing to prolong the focusing lens’s lifespan.
Maintenance of the Transmission System
During long-term cutting, smoke and dust are generated. Fine dust can enter the device through the dust cover and accumulate on the gear rack of the guide rail. This accumulation increases wear and tear on the gear rack. Gear rack guide rails are precise components, and the deposition of dust on their surfaces greatly affects the equipment’s processing accuracy. It can lead to corrosion spots on the guide rail and reduced equipment lifespan. To ensure the equipment works smoothly and product quality is maintained, thorough daily maintenance is necessary, including dust removal and cleaning. After dust removal, apply grease to the gear rack and lubricate the guide rail regularly. Bearings should also be lubricated periodically to keep the transmission flexible, ensuring accurate processing and extending the machine’s lifespan.
Operating Environment
Maintain a dry, well-ventilated workshop with a temperature range of 4°C to 33°C. In summer, prevent equipment condensation, and in winter, prevent laser equipment from freezing.
Keep the equipment away from electrical devices sensitive to electromagnetic interference to avoid prolonged electromagnetic interference. Avoid sudden high-power interference from high-power, strong vibration equipment, which can sometimes cause machine malfunctions. Such equipment includes large welding machines, giant electric mixers, and large power transmission equipment. Strong vibration equipment, such as forging presses and vibrations caused by nearby moving vehicles, can be detrimental. Obvious ground movements are particularly detrimental to precision engraving.
Other Considerations
Conclusion
Systematic and scientific maintenance can effectively prevent minor issues with laser cutting machines during usage, enhance the performance and lifespan of certain components, and, in essence, improve work efficiency.