Table of Contents
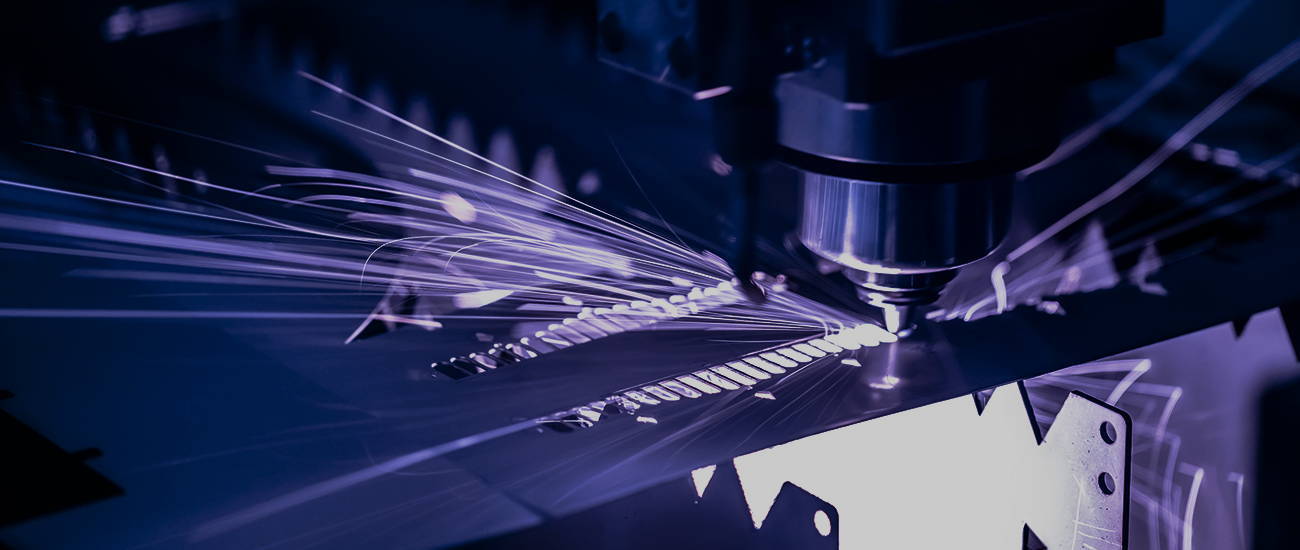
When it comes to outstanding technology in the fields of modern manufacturing and engineering, precision laser cutting is undoubtedly an area that garners much attention. This article delves into the principles, applications, and advantages of precision laser cutting to help you understand the importance and versatility of this technology.
Principles of Precision Laser Cutting

The principle of precision laser cutting is based on the concentration of high-energy laser beams. By focusing the laser beam, it can release high energy within an extremely small area, thus enabling the precise cutting of various materials. Key technological components include:
- Laser Source: Typically, either carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers or fiber lasers are used as energy sources. CO2 lasers are versatile, suitable for most materials, while fiber lasers excel in cutting metals.
- Optical Fiber: It transmits the laser beam to the cutting head, reducing energy loss while increasing system flexibility and reliability.
- Lenses: These are used for focusing the laser beam, ensuring high-precision cutting. The choice of lenses significantly affects cutting quality and speed.
- Focus Adjustment: Fine-tuning the focus position is crucial to adapt to different materials and cutting requirements.
Applications of Precision Laser Cutting
When it comes to the application areas of precision laser cutting, this technology is widely used across various industries, offering endless possibilities for manufacturers and designers. Here are some detailed insights into key application areas and the materials associated with them:

Medical Device Manufacturing
In the production of medical devices, precision laser cutting is crucial for manufacturing medical instruments, implants, and precision components. Common materials include stainless steel and titanium alloys for surgical tools and implants, while plastics and ceramics are used for various medical components.
Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry extensively utilizes precision laser cutting for cutting and shaping body parts, exhaust systems, and engine components. Primary materials include steel, aluminum, and other metals, as well as plastics and composite materials for interior and exterior components.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics manufacturing sector, laser cutting is indispensable for precise shaping of circuit boards, semiconductor components, and displays. Common materials comprise silicon, ceramics, glass, and plastics for electronic components.
Aerospace
Precision laser cutting plays a pivotal role in the aerospace sector, used for manufacturing aircraft parts, engine components, and spacecraft parts. High-strength metal alloys, titanium alloys, and composite materials are the primary materials used.
Furniture Manufacturing
In the realm of furniture manufacturing, laser cutting is employed for cutting and engraving wood, plywood, and other components, enabling highly customized furniture production.
Construction Industry
Precision laser cutting is also used in the construction sector for cutting both metal and non-metal materials to manufacture structural and decorative elements.
Advantages of Precision Laser Cutting
Remarkable Precision
Materials cut with lasers exhibit superior accuracy and edge quality compared to those cut using traditional methods. Laser cutting employs a highly focused beam, serving as a heat-affected zone during cutting, which minimizes thermal damage to adjacent surfaces. Additionally, the use of high-pressure gases (typically CO2) in the cutting process results in cleaner cuts, removing excess material from narrower workpieces and delivering smoother edges. Integrated CNC components facilitate automation, providing a more intuitive operation.
Enhanced Workplace Safety
Workplace accidents involving employees and equipment can have a negative impact on a company's productivity and operational costs. Material processing and cutting operations, including cutting, are accident-prone areas. Using lasers for these applications reduces the risk of accidents. Since it's a non-contact process, it means that the machine doesn't physically interact with the material. Additionally, the generation of the laser beam doesn't require any direct operator intervention, keeping the high-power beam securely enclosed within a sealed machine. In most cases, apart from inspection and maintenance operations, laser cutting doesn't require human intervention, minimizing the potential for employee accidents and injuries compared to traditional cutting methods.
Greater Material Versatility
In addition to cutting complex geometries with higher precision, laser cutting allows manufacturers to cut various materials without the need for mechanical adjustments, offering a broader range of thicknesses. Using the same beam with different output levels, intensity, and duration, laser cutting can cut a wide variety of metals with similar adjustments, ensuring higher precision and stricter tolerances. Integrated CNC components facilitate automation, providing a more intuitive operation.
Faster Delivery Times
The time spent on setup and operating manufacturing equipment increases the overall production cost for each workpiece. Utilizing laser cutting methods reduces the total delivery time and the overall production cost. Unlike traditional cutting methods, laser cutting doesn't require mold changes and setups between materials or material thicknesses. Setting up a laser cutting process involves more machine programming than material loading. Moreover, using laser for the same cuts can be up to 30 times faster compared to traditional saw cutting.
Lower Material Costs
By utilizing laser cutting methods, manufacturers can minimize material wastage significantly. The focused laser beam used during the cutting process generates narrower kerfs, reducing the size of the heat-affected zone and the quantity of unusable materials. When working with flexible materials, deformations caused by mechanical machine tools increase the quantity of unusable materials. Laser's non-contact cutting eliminates this issue, enabling cutting with higher precision, stricter tolerances, and reduced material damage in the heat-affected zone. Allowing parts to be placed more closely on the material reduces material wastage, lowering material costs over time.
Material Selection and Applicability
In precision laser cutting, different materials possess distinct characteristics, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right material to achieve optimal cutting results. Here are some common materials and their applicability:
- Metals: Metals are a primary application for precision laser cutting. Stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and steel are commonly used to manufacture various components due to their good thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. Different types of metals may require different types of laser sources and parameters.
- Plastics: Plastic materials, such as polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), and polystyrene (PS), have a wide range of applications in precision laser cutting. Laser cutting can create clear cuts in complex shapes and contours, making it suitable for manufacturing electronic enclosures, toys, and parts.
- Ceramics and Glass: Laser cutting is also used for cutting and engraving ceramic and glass materials. In the electronics industry, glass is commonly used for manufacturing displays, while ceramics are used for electronic components.
- Wood: Precision laser cutting is highly useful for cutting and engraving wood, which finds extensive applications in furniture manufacturing and construction. Various hardwoods and plywood can be cut and engraved to meet design requirements.
- Composite Materials: In the aerospace industry, composite materials are extensively used, typically composed of fiber-reinforced resin composites. Precision laser cutting is crucial for precisely cutting these composites to ensure part quality and performance.
Precision laser cutting technology plays a crucial role in various application areas and materials, providing efficient, accurate, and flexible solutions for the manufacturing industry. The choice of materials and their suitability depends on specific application requirements, making an understanding of different materials’ characteristics crucial for achieving the best cutting results.
Technological Development and Future Trends
Precision laser cutting technology has continually advanced and improved over the past few decades, and the future holds even more potential. Automation is a significant trend, with automated systems enhancing production efficiency and reducing operator intervention. This means that more complex tasks can be executed by machines, reducing human errors and improving manufacturing consistency.
Furthermore, higher-power lasers and advanced optical systems will further expand the applications of laser cutting. High-power lasers can cut thicker materials more rapidly, broadening the scope of precision laser cutting. Simultaneously, continuous improvements in optical systems make laser focus more precise, enabling higher cutting accuracy.
Sustainable manufacturing and green technology will also drive the development of precision laser cutting technology. As laser cutting reduces waste production, decreases reliance on natural resources, and minimizes environmental impact, it plays a crucial role in a company’s sustainability efforts and social responsibility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, precision laser cutting technology stands as a vital tool in the modern fields of manufacturing and engineering. Its principles and technology make it widely applicable across industries, offering a combination of high precision, speed, material versatility, and resource efficiency, making it a preferred method for many businesses. Precision laser cutting not only enhances production efficiency but also provides innovation and a competitive edge for manufacturers.
In the future, precision laser cutting technology will continue to advance and expand into more fields. Automation, higher-power lasers, and sustainable manufacturing will drive these advancements, positively impacting society and the environment. We encourage readers to explore and apply this significant technology to meet evolving market demands, drive innovation in the manufacturing industry, and promote sustainability. Precision laser cutting will continue to play a critical role in manufacturing, contributing to our lives and industrial progress.