Table of Contents
Introduction

Laser welding technology represents a new era in industrial innovation, leading the industry with its unique welding approach. Laser welding machines can weld refractory materials and perform welding on dissimilar materials, yielding excellent results. Its notable features include high welding speed, deep penetration, and minimal heat distortion.
Challenges in Welding Dissimilar Metal Materials

Differences in Melting Points
Welding becomes challenging when there is a significant difference in the melting points of various metal materials. Lower melting point materials can melt while higher melting point materials remain in a solid state, leading to issues such as material loss, alloy element burning, or evaporation, making the welding joint difficult to form.
Differences in Coefficient of Linear Expansion
Welding becomes difficult as the coefficient of linear expansion varies among different metal materials. Materials with a higher coefficient of linear expansion experience more significant shrinkage during cooling, resulting in substantial welding stress during crystallization of the weld pool.
Differences in Thermal Conductivity and Specific Heat Capacity
Variations in thermal conductivit and specific heat capacity among different metal materials can deteriorate the crystallization conditions of the weld metal. This leads to severe grain coarsening and affects the wettability of refractory metals.
Advantages of Laser Welding Machines in Welding Dissimilar Metal Materials

Laser welding machines effectively address the challenges encountered in welding different metal materials. The high cooling speed and minimal heat-affected zone provided by laser welding create favorable conditions for welding materials with different structures after melting. Metal composite components manufactured using laser welding methods can not only fully leverage the excellent properties of each constituent material but also significantly reduce production costs, allowing for the maximization of material performance.
Small Focus and High Power Density
Laser welding machines, with their small focus and high power density, are capable of welding high-melting-point and high-strength alloy products.
Non-contact Processing
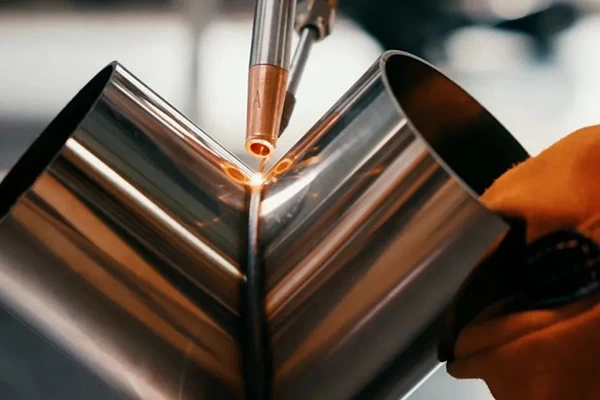

Laser welding is a non-contact process, eliminating the wear and replacement of specialized tools. The kinetic energy and movement speed of the laser beam can be adjusted, allowing for various laser welding processes.
High Automation Level
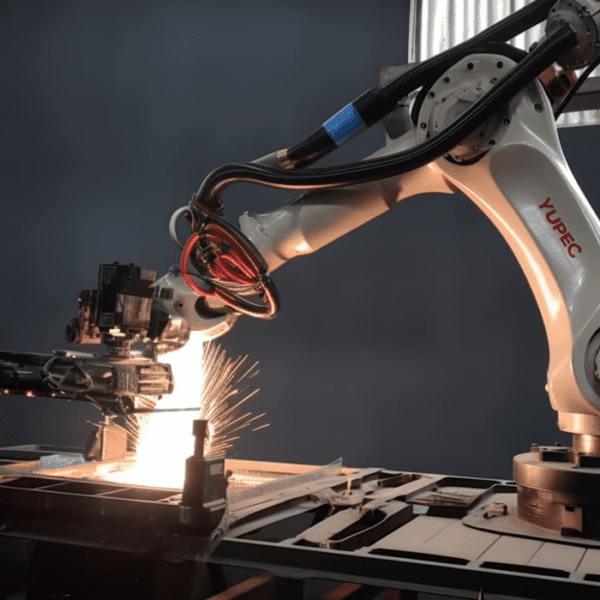
Laser welding machines can be easily adjusted via computer control, ensuring fast welding speeds, high efficiency, and the capability to effortlessly achieve complex laser welding patterns.
Narrow Pulse Width and Small Heat-Affected Zone
Laser welding features a narrow pulse width and small heat-affected zone, making it suitable for welding thin sheets.
Applicability in Vacuum Environments
Laser welding is applicable to products within vacuum environment containers and the internal structures of complex structures using a glass ionization laser.
Easy Guidance and Focusing of Laser Beam
Laser beams are easy to guide and focus, allowing for multi-directional transformations.
Wide Range of Adjustable Frequency and Pulse Width

Laser welding machines offer a broad range of adjustable frequencies and pulse widths to meet the welding requirements of various materials.
Application of Laser Welding Machines in Welding Dissimilar Metal Materials
In the field of metal welding, laser welding is widely applied to the welding of metals and their alloys, such as steel, iron, aluminum, and copper. So, what are the common metal materials used when we use laser welding technology?
Stainless Steel Welding Application
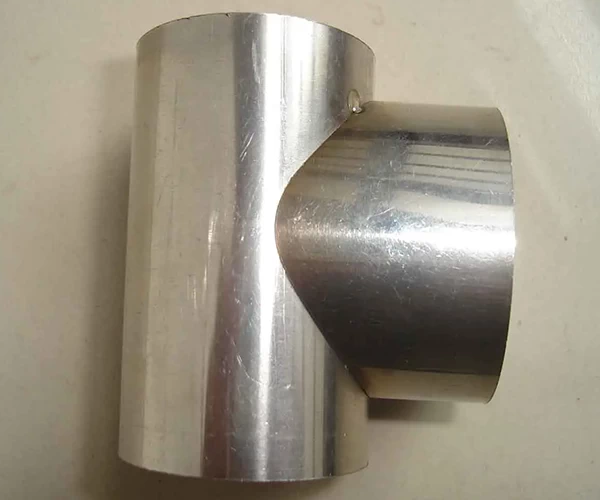

Stainless steel finds extensive applications in various industries, including food processing, medical devices, and chemical equipment manufacturing. Laser welding technology demonstrates exceptional performance in stainless steel welding. Firstly, laser welding provides highly precise control, ensuring excellent weld seam quality, making it suitable for food processing equipment with strict hygiene standards. Secondly, laser welding allows for rapid task completion, enhancing production efficiency, which is crucial for the large-scale production of stainless steel components.
Aluminum Alloy Welding Application
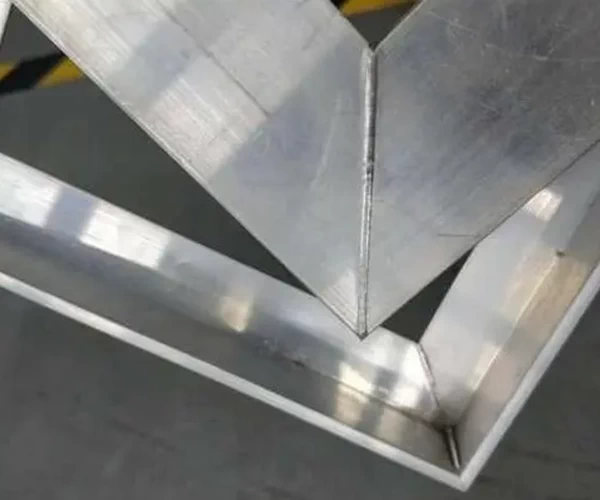

In the aerospace and automotive manufacturing sectors, aluminum alloy is favored for its lightweight and high-strength properties. However, traditional welding methods may lead to issues like porosity and cracks when dealing with aluminum alloys. Laser welding technology, with its high energy density and instantaneous heating characteristics, effectively overcomes these challenges. Laser welding offers a minimal heat-affected zone, reducing the risk of deformation, and boasts fast welding speeds, making it suitable for efficient welding of large aluminum alloy structures.
Titanium Alloy Welding Application
The use of titanium alloys in the medical and aerospace industries is increasing, presenting challenges due to their high melting point and thermal sensitivity. Laser welding technology, employing localized heating, effectively avoids excessive heating of the entire workpiece. This precise heat control ensures high-quality weld seams, particularly suitable for applications in the medical field where stringent welding quality requirements exist.
Application of Other Metal Materials
Laser welding technology extends beyond common metal materials and is applicable to materials like nickel alloys and copper. Nickel alloys are frequently employed in the chemical and aerospace industries, demanding high-quality welding due to their high strength and corrosion resistance. Laser welding, with its high energy density and localized heating features, provides an ideal solution for welding nickel alloys.
In summary, laser welding technology exhibits high production efficiency, stable and reliable processing quality, and economic and societal benefits. As we navigate an era of constant innovation in equipment, materials, technologies, and processes, understanding the versatility and advantages of laser welding becomes crucial for staying at the forefront of technological trends.
Conclusion
In conclusion, laser welding technology excels in high production efficiency, stable and reliable processing quality, and positive economic and social benefits. In the ever-evolving era of new equipment, materials, technologies, and processes, producers must not only understand the characteristics, advantages, and requirements of laser welding but also recognize the numerous innovations and future trends in this field. Only then can they stay at the forefront of technological trends.